Want to get information from Google without using code or paying for tools? This handy guide will show you exactly how to get web scraping Google search results data into a neat Excel or CSV file using simple, free, and no-code methods.
If you're doing keyword research, market analysis, competitor tracking, or content planning, this simple step-by-step guide will help you collect the data you need quickly and reliably. Whether you're looking at one search result page or lots of search results, you'll learn how to automate the process as much as possible using no-code automation tools. You won't need any technical skills or complicated setups.
What is Google SERP?
The Google SERP (Search Engine Results Page) is the full page of search results that Google displays after you enter a keyword. In other words, it's the entire page that a user sees after performing a search. It includes everything related to the user's query. This could be webpages, summaries, AI overview, maps, images, videos, ads, and more.
To improve the search experience, Google continually updates and refines the SERP. In the early days, it only showed a simple list of links related to what you were looking for. Today, it has lots of different features and elements designed to help users quickly find the most relevant and useful information for their search.
What data can you get from Google search results and who needs it?
When you scrape google results, you are after structured, repeatable pieces of information that can be stored in a sheet or database. Depending on the SERP type, you can extract:
AI Overview
AI Overview is a new Google Search feature that adds “generative AI summaries + multi-source aggregation” directly into the search results. It gives you a consolidated answer instantly, so you don’t have to open multiple webpages to find the information yourself.
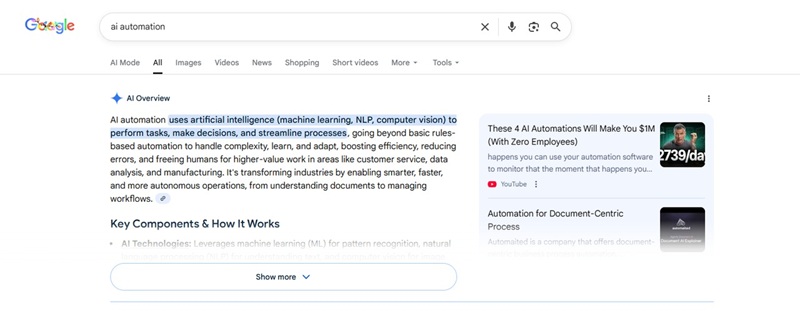
Ads
Ad headline
Display URL
Description
Ad position (top, bottom)
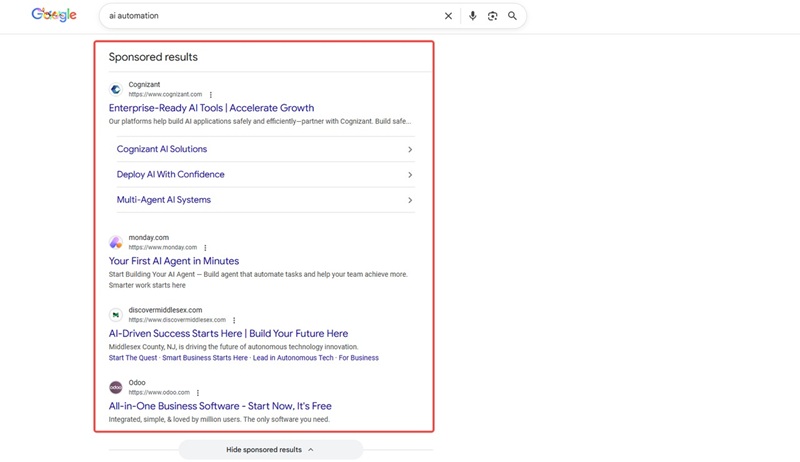
Organic results
Page title
URL
Meta description or snippet
Displayed site name or breadcrumb
Sitelinks (when present)
Date (for articles, sometimes shown)
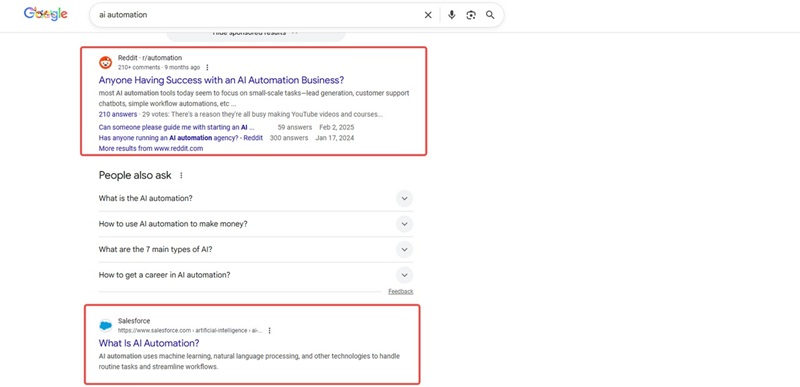
Local pack
Business name
Rating and review count
Category (e.g., “Italian restaurant”)
Address and phone number (sometimes)
Price level and opening hours (where shown)
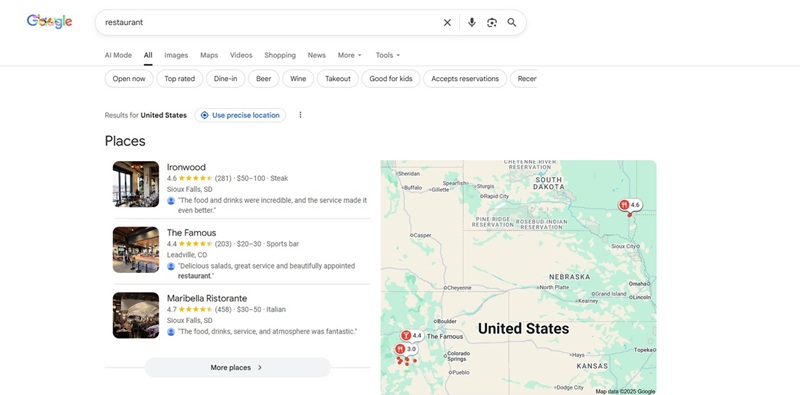
People Also Ask
Question text
Short answer snippet
Source URL for the answer
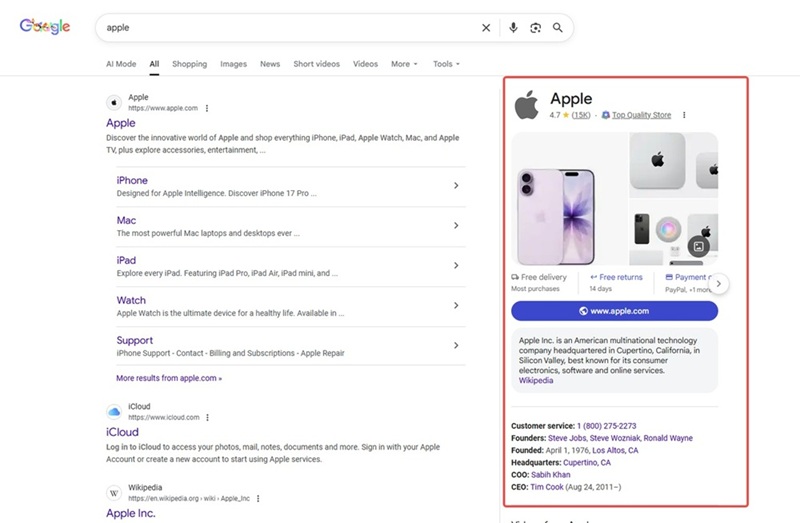
Knowledge Panel
A Knowledge Panel is an information box that appears on the right of desktop results or at the top of mobile results. It gives a short, clear summary of a specific thing, like a person, company, place or book. Knowledge Panels can improve the user experience and make brands or individuals more visible and trustworthy.
Other SERP features
Featured snippet text and source URL
There are "AI automation" image or video titles and links
Top stories headline, source, and URL
Who uses this data?
Almost anyone making decisions based on visibility in search can benefit from structured data extracted from SERPs.
SEO specialists: to monitor rankings, track SERP features, and understand competitors.
PPC managers: to see which competitors are buying ads, what messages they use, and how often they appear.
Content marketers: to map user intent, identify topics, and see featured snippet patterns.
Local businesses and agencies: to monitor local pack presence across locations.
Market researchers: to analyze how brands are represented on search for key terms.
Product and growth teams: to track brand visibility, review presence, and user questions in People Also Ask.
How to scrape Google search results without coding skills?
Prerequisites
Download the Automa desktop app
Sign up for an Automa account using any email address. The same account works on both the web and the desktop app. You can also sign in directly with your Google email or GitHub account.
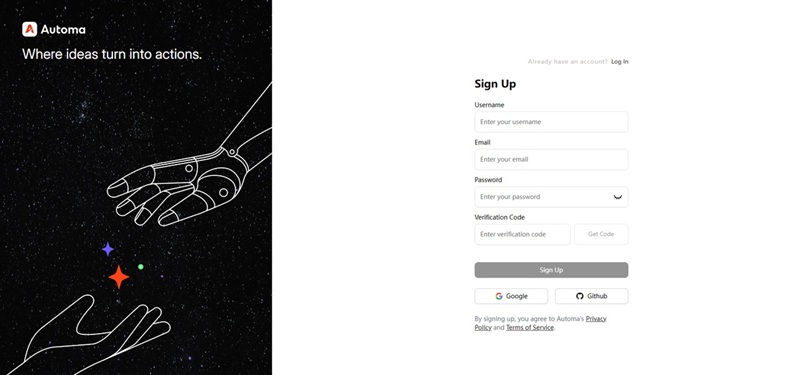
Step 1 Get the Google search results scraping tool
After logging in to your Automa account, click “Get”. The Google search scraper will be saved to your Automa client.
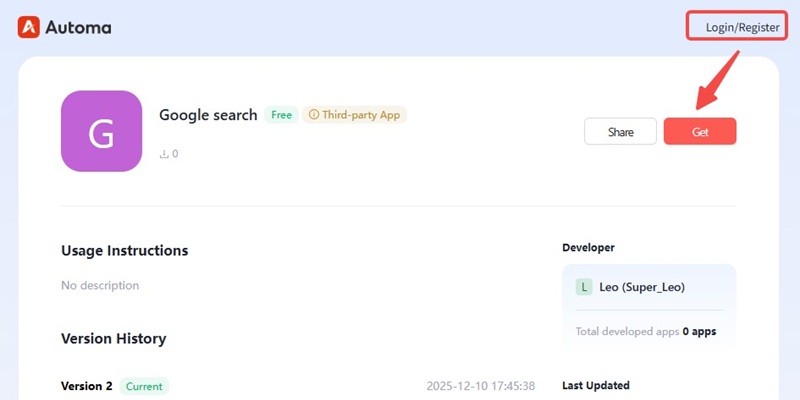
Step 2 Log in to Automa and install the browser automation plug-in
Sign in to the Automa desktop app using the account you just created on the website. Click the profile icon in the upper-right corner, navigate to “Tools,” and then select “Automation Plug-ins.”
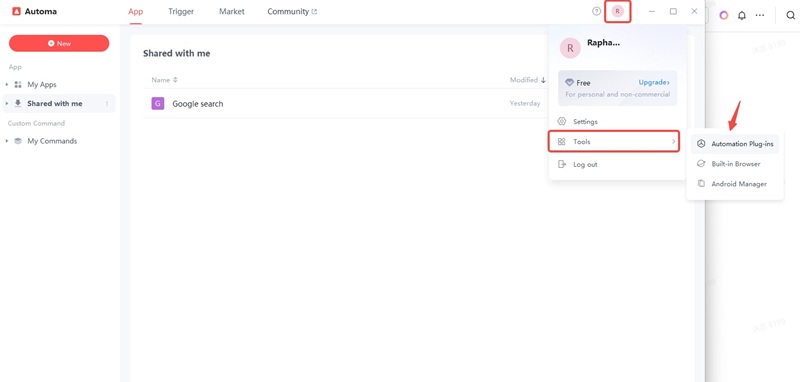
In the pop-up window, find “Google Chrome Automation” and click “Install.” The Automa automation plug-in will then be installed.
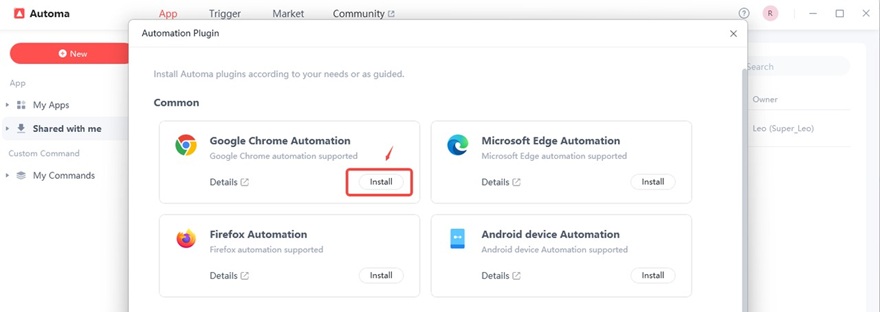
Step 3 Run the Google Search Results Scraper
In the left navigation panel, click “Shared with me”. On the right, you’ll see the app you saved. Click the play button to run the program
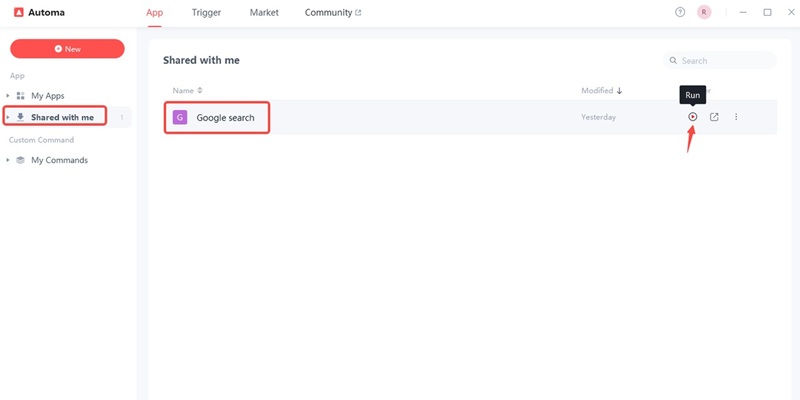
Step 4 Enter your target keywords
In “Quantity acquired”, enter the number of Google search result links you want to scrape (the maximum is 100). Then, type your target keywords into the box—for example, we’ll use “web automation”, Click “Done”, and the app will start running.
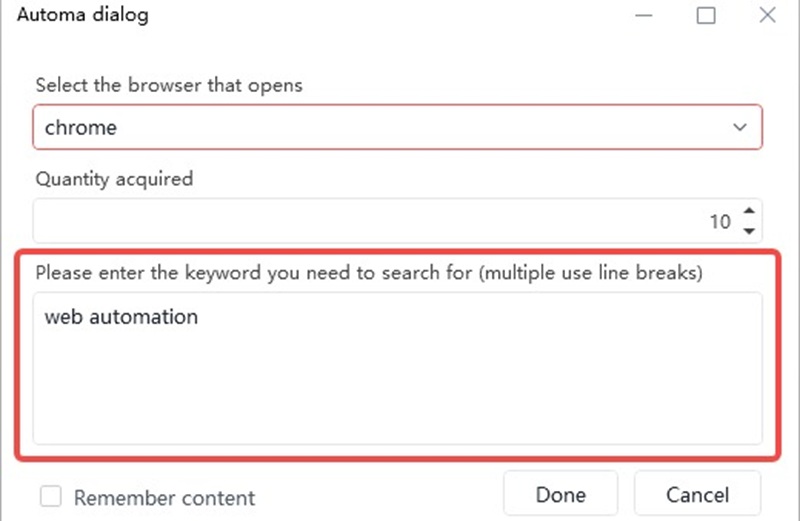
Step 5 Get your Excel file
Once the program finishes running, locate the Excel file named “Results_obtained” on your desktop. Open the file, and you’ll have the Meta titles, Meta descriptions, and URLs of the top 10 pages for the keyword “web automation”.
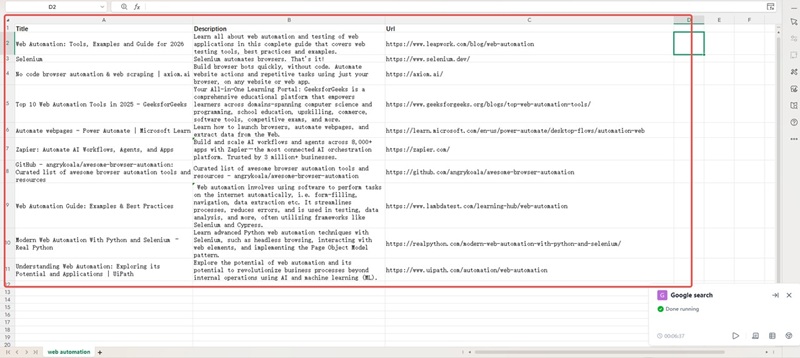
All you need to do is enter your keywords, and you can get the SEO competitor information you want, greatly reducing the time spent on data collection and organization. Try the Automa RPA tool now, and focus more on content creation to quickly grow your traffic and business.
Why Scrape Google Search Results?
If you start to think of Google search results as data, not just webpages, you'll see a whole new range of uses for them. Scraping Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) is not just about curiosity. Google indexes a huge number of public webpages that can provide valuable data insights to support business and research decisions. There are several reasons why people scrape Google SERPs.
Getting the right SEO info
Google doesn't share its ranking algorithm, so scraping the SERP is an effective way to understand real search performance. By collecting information about how well websites are doing in search engine results, what their competitors are doing, how search engine results pages (SERPs) are different depending on the user's location or device, and other features, businesses can make an informed decision about their SEO strategy. This also helps to see when rankings go up or down and to find out why.
Advertising analysis (SEM)
SERP data can show which competitors are bidding on the same keywords, their ad copy and landing page strategies, ad share, and traffic distribution between paid and organic results. This information is very useful for improving paid campaigns and for comparing results with competitors.
Finding new opportunities
By looking at the "People Also Ask" boxes, related searches, search intent types, and content format distribution on the SERP, businesses can find new user questions and interests. It also helps you find missing content types, like videos, FAQs, or in-depth guides. It gives you tips for making content, improving product pages, and developing topics.
Competitive intelligence
Scraping SERPs lets companies see how their competitors' rankings change, check their titles, descriptions and content strategies, and spot new pages, features or attempts to occupy special SERP features (like Featured Snippets or Local Packs) quickly. This data is very important for competitive intelligence and helps to make sure that strategies are up to date.

Brand monitoring and reputation management
By checking brand-related search results, companies can see negative news about their brand, changes in reviews, competitor brand ads, and how Google displays brand panels and ratings. This helps PR, growth and marketing teams to manage risk and protect their reputation.
Local SEO tips
Scraping Local Pack data provides information on local competitors' ratings, review counts, pricing, business hours, Google Map rankings, and regional SERP differences. These insights are very important for chain stores and local businesses.
Once you've got your SERP data in a simple list, you can filter, sort and visualise it. This makes it much easier to answer questions that are almost impossible to deal with manually when you're dealing with a lot of data.
Challenges in scraping Google search results
Scraping Google is not like scraping a simple static website. Google invests heavily in protecting its infrastructure and user experience. Trying to scrape too aggressively or naively will trigger defenses quickly. Key challenges include:
Anti‑bot detection: Google uses multiple signals to decide whether traffic looks human: request rate and patterns, IP reputation and geography, browser fingerprint (headers, JS behavior), and interaction signals. If your traffic looks suspicious, you will see CAPTCHAs, temporary blocks, or “unusual traffic” messages.
Dynamic and personalized results: SERPs vary by location (country, city, even neighborhood), language and device type, search history and personalization. For consistent data, you need to control these variables explicitly by setting location, language, and sometimes using fresh sessions.
Frequent layout changes: Google continually experiments with new layouts and SERP features. A selector that identifies a title today may break next month.
Tips for scraping Google without getting blocked
Rotate IP Addresses Aggressively
To avoid seeing captchas, temporary blocks, or even long-term bans., route your traffic through a large pool of proxies so that every request (or at least every few requests) appears to come from a different user. A smart IP rotation system that uses residential and mobile proxies will work best, as those look like real users’ devices from Google’s perspective. With proper IP rotation in place, your requests will blend in with normal search traffic, dramatically reducing the chances of getting blocked.
Randomize Your Request Timing
No real user sends a perfectly steady stream of requests to Google 24/7. Instead of firing off a request every second, introduce randomness into your delays. For example, wait anywhere between 2–7 seconds between requests. This helps your scraper resemble normal human browsing behavior and avoids triggering rate limits.
Avoid Scraping the Same Query Repeatedly
Constantly requesting the exact same search query or URL is suspicious behavior. People vary their searches, click through to different pages. If you must re-check the same query, spread those checks over time, mix them with other queries, and avoid fixed schedules.
Conclusion
If you know how to get information from Google search results without using any computer code, you can get lots of useful information for research, marketing, SEO and competitor analysis.
With the Automa no-code tools, you can perform web scraping of Google search results, collecting search results, URLs and descriptions easily and quickly. With a few clicks, you can turn the pages of Google results into a neat list that you can filter, analyse and add to your reports or dashboards.
If you want to validate content ideas, then no-code Google SERP scraping is for you. It will help you work faster, smarter, and with much more confidence in your data.
FAQs
Is it legal to scrape Google search results?
The legality of scraping Google search results is complicated. While the law in the US says that generally, accessing data that is public does not count as a crime under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA), it breaks Google's rules and can lead to serious consequences. These include being banned from the internet, losing your account, and being taken to court for breaking the contract. Also, if you bypass the technical security measures (like CAPTCHAs), you are much more likely to face legal risks. In fact, you could even be breaking the law by violating the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). So, this practice is very risky from both a civil and technical perspective. Another important point is that the data you get must not be used to make money.
Is there an official Google Search API?
Yes, Google officially provides a custom search JSON API. This allows developers to programmatically retrieve search results for specific web pages or websites. They can do this by configuring a programmable search engine. This service is free for 100 queries a day, and there is a paid option for $5 per 1000 queries, but you can only make 10,000 queries a day. Although there is an API, it's rarely used. It's expensive and can only crawl a few websites. It takes a long time and a lot of effort to make changes to a website, so it's not worth the trouble.
Can I scrape Google for free without coding with Automa?
Absolutely! You can use Automa RPA for free and without writing any code, to scrape Google search results by building a simple drag-and-drop workflow. Or you can use the app in Automa's "Market." When you run the app, you just type in some keywords and you'll get a spreadsheet with your Google search results.
What is the easiest no-code tool to scrape SERPs?
Automa is the simplest and easiest-to-use no-code search engine results page (SERP) crawler available, thanks to its visual drag-and-drop interface that allows users to extract search results without having to write any code. It uses "smart capture" technology to make the process easier. This technology automatically detects and selects list patterns (such as titles, links, and summaries) on a page with a single click. It also has a strong app marketplace with ready-made templates for Google, Bing, and Amazon. By automating and simulating how a person interacts with a computer, like a real web browser, it can naturally handle web pages loading quickly, making it easier to learn than traditional coding frameworks and ideal for beginners.
Can I use AI to scrape Google?
AI can help, but it does not replace the underlying scraping mechanism. You still need a way to fetch SERP HTML or structured results. Where AI shines is:
Cleaning and normalizing scraped data.
Classifying intent, sentiment, or topic of results.
Summarizing SERP content into human‑readable insights.
Think of AI as a layer on top of SERP data collection, not a substitute for the process that actually gathers google search results.

